
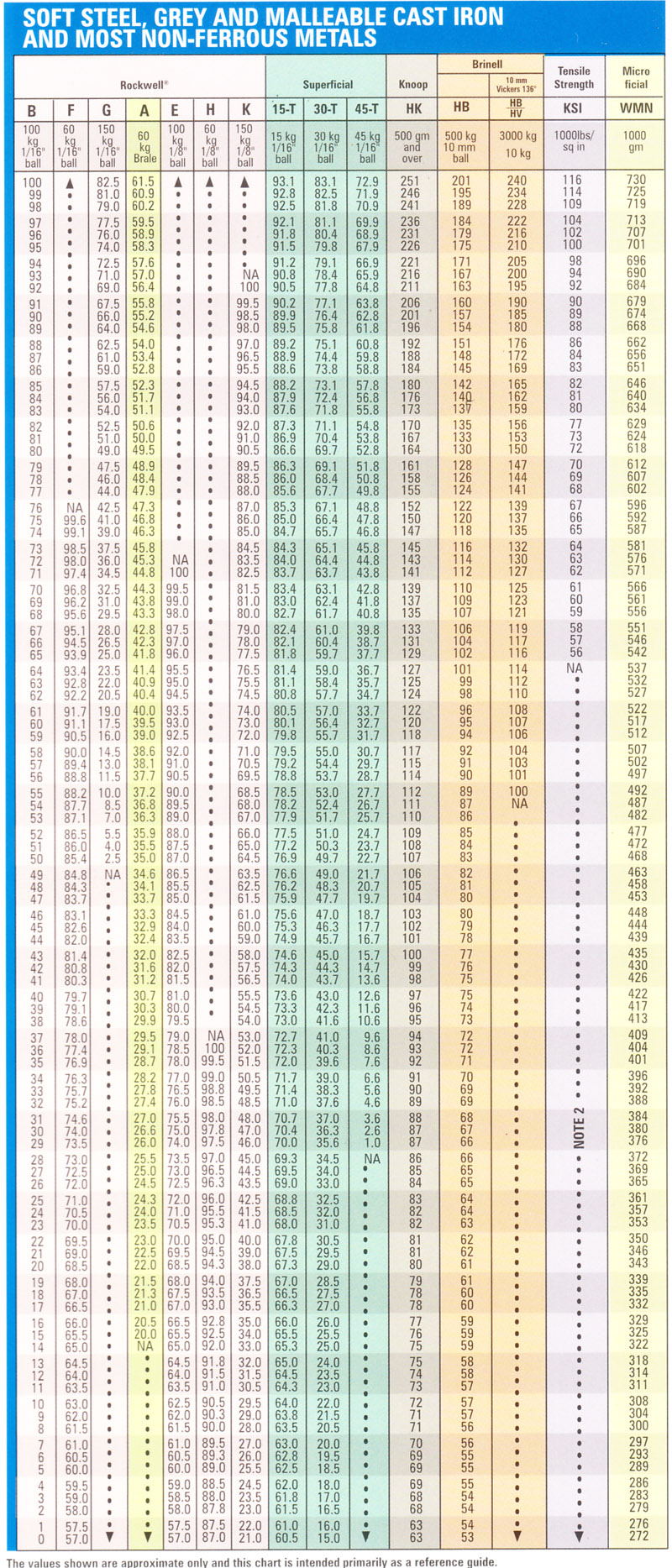
However, by comparison of the hardness values at different scales, one can convert one hardness measure to another. Therefore separate conversion tables are neccessary for different materials.ģ) Brinell Hardness numbers in parentheses are outsite the range (HB>630) This limit is set to avoid errors introduced by the deformation of the ball indenter itself.Įxact conversion of the hardness values obtained using various hardness scales in general is not possible. The modulus of elasticity and the depth of indentation influence conversions. The accuracy of the conversion depends on the accuracy of the provided data and the resulting curve-fits.Ģ) Indentation hardness is not a single fundamental property but a combination of properties, and varies with the type of test. ASTM E 140 – 97, September 1999, Conversion for Non-Austenitic Steels, Table 1.


The Vickers hardness ( HV) is calculated using the following Vickers hardness formula:ġ) Standard Hardness Conversion for metals acc. Further information regarding existing standards and procedures can be found in references. Schematic representation of the Vickers test is shown in Figure 1. At low values (VH<~400HV), Vickers hardness was shown to be the same as Brinell hardness (see hardness conversion section). Another advantage of the Vickers hardness test is absence of different scales, as compared to Rockwell and Brinnell tests. In contrast with Rockwell and Brinnell hardness techniques, the pyramid indenter is advantageous since the square imprints are easier to measure than the round impressions from spherical and conical indenters. Imprint size is measured with the aid of optical microscope, see the figure below. A square-based pyramid indenter whose opposite sides meet at the apex at an angle of 136° is employed in Vickers hardness test. Hardness may vary as a function of load, therefore, it is advised to specify applied when HV hardness is reported. In the test, a minor load (10 kgf) is first applied, and the test dial (measuring the indention. The harder the material, the higher the HR reading. A diamond pyramid is pressed against the solid with a certain normal load and the hardness is calculated based on the imprint left on the surface. The Rockwell Hardness Test presses a steel or diamond hemisphere-conical penetrator against a test specimen and measures the resulting indentation depth as a gage of the specimen hardness. The Vickers Hardness test (ISO 6507) is used to characterize hardness of various solid materials (metals, ceramics, etc.). Vickers Hardness Test: Vickers hardness test Hardness and tensile strength do not apply to nonferrous metals, with the possible exception of certain aluminum alloys.Figure 1. The above formulas give the tensile strength in pounds per square inch for steels. Tensile strength = Bhn × 490 (for Brinell numbers larger than 175) Tensile strength = Bhn × 515 (for Brinell numbers up to 175) These Conversion Tables presents data in the Rockwell A, B, C, D, E and F hardness range on the relationship among Brinell hardness, Vickers hardness, Rockwell superficial, hardness, and Shore Scleroscope hardness of nonaustenitic steels including carbon, alloy, and tool steels in the as-forged, annealed, normalized, and quenched and tempered conditions provided that they are homogeneous.įor plain carbon steels, the approximate relationship between the hardness and tensile strength is: Brinell and Rockwell Hardness Conversion Table Chart


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
